What are the Intellectual Property Laws in India?
Intellectual Property is the intangible original creation of your mind, which can act as a valuable asset in this competitive business world. They are regulated and protected by various intellectual property laws in India. In this blog, we explain the nitty gritty of all such IPR Laws in detail.
Intellectual property (IP) laws are designed to protect the rights of creators and innovators over their creations and inventions. The laws governing IP provide a framework to businesses as well as individuals that helps safeguard the moral and economic rights of creators and promotes creativity and innovative work that can contribute to better economic growth. In India, IP laws protect a wide array of rights; patents, copyrights, and trademarks, are the primary ones.
The businesses, entrepreneurs, and individuals who are involved in innovation work must have a sound understanding of IP laws. Such individuals or entities must register their work under relevant IP law to protect their innovative creations from any misuse or unauthorized use by any individual or third party.
What is Intellectual Property?
Intellectual Property (IP) refers to a kind of intangible asset that is the outcome of the human intellect. This intangible asset also has a commercial value. There are various forms of the Intellectual Property that can serve as an intangible yet financially viable asset for their owners, individuals or businesses.
Types of Intellectual Property
Intellectual Property has numerous forms; some common types of Intellectual Property are described below;
Trademark: This form of IP includes Names, Logos, Labels, Theme Music, Slogans, Website Domain Names, etc. which is responsible for representing the identity of an individual or a business entity.
Patent: In this form of IP, there are any new inventions or newly invented products, or processes.
Copyright: Original Literature work, visual art, and performing art, etc. fall under the category of Copyright IP.
Design: As the name suggests, this IP possesses specific design features of a product such as a peculiar shape, size or even color/color combination.
In order to protect these IPs, there are various IP laws in India allowing the owners to protect and regulate how their intellectual properties can be used, who can access them, and how they can be monetized. This legal protection can come in a lot of ways, depending upon the type of intellectual property involved. All these types of legal protections and their respective IP Laws are discussed in the blog further. But, before moving forward to the next section, let’s look at some of the popular examples of Intellectual Properties.
Intellectual Property Examples
Examples of intellectual property may include patents for inventions such as the telephone, copyrights for a song, painting, a business/professional or individual logo or tagline, and any specific shape related to a product. With the help of these examples, you can understand how Intellectual Property can have significant commercial value which makes it important to protect these intangible properties using IP laws in India.
What is Intellectual Property law in India?
India is a country having a complicated and vast legal framework for safeguarding intellectual properties through a number of Intellectual property laws; the Trademark Act, the Copyright Act, the Patents Act, and the Design Act to name a few. The core purpose of Intellectual Property laws is to give legal protection to all kinds of intellectual properties and thus, foster innovation and creativity across various sectors.
By providing legal protection for Intellectual Property, such laws encourage innovation by supporting individuals or entities through financial incentives to invest in creative ideas and innovations. Due to the lack of such protection, individuals/businesses won’t spend their time and resources to develop new or innovative products or processes, after knowing that their hard work could be easily copied or used by others to make a profit without any legal restraint.
Different Types of Intellectual Property Rights
The different types of IPR are offered by various intellectual property laws in India. These laws mainly include Trademark Act, Copyright Act, Design Act, and Patent Act; each granting legal protection and remedies to the owners of trademarks, copyrights, industrial designs, and patents respectively against any potential misuse, infringement or theft. The section gives an overview of such IP Acts including purpose, requirement for registration, and the enforcement of rights through civil and criminal proceedings.
The Trademark Act
The Trademark Act is the law dedicated for the regulation of registration and legal protection of trademarks in India. Trademarks are symbols, words, phrases, or device marks used to identify and distinguish the identity of an individual or business entity. Some examples of Trademarks are brand names, legal names, trade names, logos, label marks, slogans, and also sounds & combinations of colors.
The primary objective of the Act is to protect such trademarks against misuse, forgery, and deception in the marketplace, by giving their owners the exclusive rights to their ownership and usage. In other words, the Act offers remedies to the owners of registered trademarks against a potential theft or infringement of IPR rights.
Besides, the Act also defines what can and cannot be registered as a trademark and sets out the procedure to be followed for trademark registration in India. Once a trademark is registered, it remains valid for a period of ten years, after which it can be renewed by following a separate renewal process, also mentioned in the Trademark Act.
The Copyright Act
The Copyright Act is a kind of IP law that governs the registration and legal protection of copyrights in India. These rights are defined under the Act as an exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and perform an original work of authorship i.e. original piece of literature, music, script, song, drama, art, cinematographic film or audio tune, etc.
Although registration under the Copyright Act is not mandatory for Copyright protection, it can still be obtained for availing certain benefits like possessing legal evidence for ownership of the copyrighted work and being enabled to sue any third party for the infringement of rights provided to the owner under the Copyright Act.
As far as the validity of the Copyright Registration is concerned, for literary, dramatic, musical, and artistic works (other than photographs), the registration lasts for the lifetime of the author plus 60 years after their death. In the case of photographs, the validity of the copyright lasts till the lifetime of the author and additionally 60 years more after their death. However, if the photograph is published, in that case, the copyright lasts for 60 years from the publication year. In the case of cinematographic films, sound recordings, and government works, the copyright lasts for 60 years from the year of publication. Upon expiration of the copyright term, the work comes to the public domain which can be freely used by any individual/business without requiring any kind of legal permission or authority and is not liable to pay anything to the original copyright owner.
The main objection of the Copyright Act is to encourage creative or innovative practices across the nation along with dissemination of knowledge by offering incentives to the creators who are working towards generating more new original, unconventional and useful works.
The Design Act
The Industrial Design Act is a law that governs the registration as well as protection of industrial designs in India. In this law, an Industrial design is defined as a unique and specific feature of shape, configuration, pattern, ornamentation, or composition of lines and colors or color combination of any product in two-dimensional or even three-dimensional.
The Act fosters innovation and creativity in industrial design by providing legal protection to the owners of such designs against any fraud or misuse. Its purpose is to ultimately incentivize designers and manufacturers to invest time, resources, money and resources into creating new designs at the end of the day.
Apart from that, it sets out the need for an industrial registration design including that the design must be novel, original and must not be formerly published or used in India. The process of filing this registration involves submitting an application with the Indian Patent Office with the required payment fees. Upon successful registration, the owner of an industrial design will have the exclusive right to use his designs and prevent others from using it without permission for as long as 10 years from the date of Registration.
The Act also provides for the enforcement of IP rights of the Industrial design, through civil and criminal proceedings. In the case of infringement of his IP rights, the design owner has the legal right to claim remedies from the infringer such as injunctions, damages, and account of profits. In addition, the Act also has the provision of criminal penalties, including fines and imprisonment, for intentional infringement of rights by an individual or business.
The Patent Act
The Patent Act is a law governing the registration and protection of patents in India. A patent is a legal right granted to the investors or creators of a new, useful, and non-conventional product or process, the exclusive rights to produce, use and sell their invention for a certain predefined period. The core purpose of this act is to promote innovation and technological advancement in India by offering new & innovative product owners a legal structure granting them legal rights to safeguard their innovations against any misuse or forgery.
The Act allows you to register your new or innovative creation with the Indian Patent Office and possesses requirements for patentability i.e. novelty, non-obviousness, and utility. On successful granting of the patent, it provides the owner with some exclusive right to use, manufacture, and/or sell the invention for a period of 20 years from the date of filing, and also makes sure that the renewal fees for the patent are paid every year.
The Act also offers the enforcement of patent rights through civil and criminal proceedings and sets out penalties for breaching those rights. In case of infringement of a patent, the patent owner can seek remedies i.e. damages, injunctions, and account of profits. On the other hand, the infringer will have to bear criminal penalties in the condition of intentional infringement of patent rights including fines and imprisonment.
Purpose of Intellectual Rights
The main purpose of the Intellectual Property (IP) law is to safeguard the rights of creators and innovators by providing legal frameworks for the ownership, use, and commercialization of their intellectual creations. Intellectual Creations in India include trademarks, patents, copyrights and other forms of innovative expression.
In India, Intellectual Property laws offer a plethora of benefits to different stakeholders such;
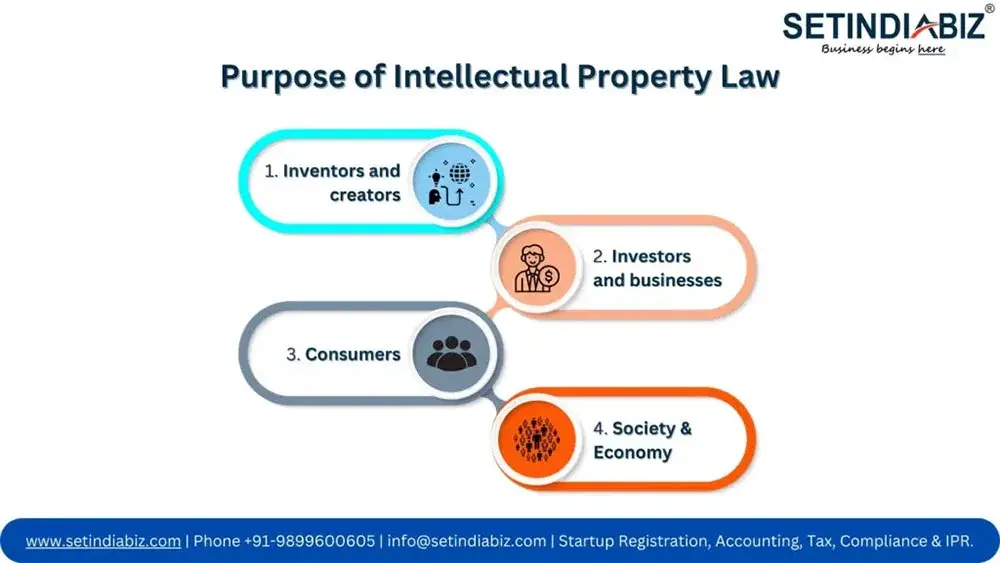
1. Inventors and Creators
Intellectual Property laws offer legal protection to inventors and creators by providing them exclusive rights to safeguard their creations. The law assures them that they can benefit from the commercial use of their ideas and prevent others from using their creations without their consent or permission.
2. Investors and businesses
Intellectual Property laws give investors or businesses the assurance to invest in and develop non-conventional and innovative products & processes. They can rely on the protection provided by these laws to recover their investment and profits.
3. Consumers
Intellectual Property laws for consumers ensure that they can take benefits of good quality and innovative products as well as services. They also encourage competition and the development of new technologies which lead to better products and services for consumers.
4. Society & Economy
IP laws foster creative work and innovation that contribute to overall development of the economy of a nation. They also help to safeguard traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, important for the preservation of cultural heritage.
Conclusion
In India, the Intellectual Property regime has witnessed significant changes in recent years, making it more effective in protecting the rights of various stakeholders. By providing legal protection and enforcement mechanisms, IP Laws in India have contributed significantly to encourage investment, research & development, technology transfer and trade. In addition, IP laws push businesses & individuals to monetize their ideas and inventions, thus accelerating economic growth leading to a prosperous nation. It’s must to have IP Laws in India to make ways for innovations and thus, acceleration of economic growth.