Top 7 Benefits of One Person Company in India
The purpose of this blog is to provide detailed insights into the benefits of One Person Company in India. Also, we have compared the benefits with disadvantages of OPC to present a clearer picture of its suitability for startups.
Understanding the benefits of One Person Company is crucial if you’re a single owner or entrepreneur and looking forward to starting your own company in India. A One Person Company helps you gain full control of your business and gives you the entitlement to all its profits. Despite being the only owner, your liability in a One Person Company is limited to the subscribed capital amount only. Moreover, its mandatory registration with the Registrar of Companies, gives it a distinct legal identity enhancing its credibility and growth potential in the market. The benefits of One person Company are not only huge but also practical. However, before we delve deeper into its details, let’s understand what a One Person Company really is!
What is a One Person Company?
A One Person Company is a type of Private Limited Company defined under Section 2 of the Companies Act of 2013 as having a single member only. This means that a One Person Company is owned by a single shareholder who is entitled to all its shareholding and profits. Since the company operates as a Private Company, its shares cannot be sold on public platforms like stock exchanges, or to the general public at large.
Moreover, the company offers limited or restricted liability to its single shareholder, which implies that the shareholder is only liable to pay the amount of the capital he has subscribed in times of financial crisis, and not a single penny more than that. This is a huge benefit a one person company offers compared to its counterparts like Sole Proprietorships which does not restrict the liability of its only proprietor in any sort. To become a shareholder of a One Person Company, you must be
- An Individual
- An Indian Citizen
- A Non-Minor
Company Registration
Is One Person Company Registration Mandatory?
Yes, One Person Registration is mandatory under the Companies Act of 2013. For registering a One Person Company, an application has to be filed to the Registrar of Companies through the online portal of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs ( mca.gov.in ). Registration grants a distinct legal identity to the One Person Company and offers loads of other benefits which we will discuss in the further sections. Since registration is compulsory, it is obvious that establishing and operating a One Person Company without registering it is illegal and can potentially expose both the company and its members to adverse legal consequences. Eventually, it may also result in your company getting shut down by relevant authorities.
Top 7 Benefits of One Person Company in India
The benefits of One Person Company not just extends to its sole shareholder, but to all other stakeholders, including its creditors, customers, and regulatory authorities. The shareholder benefits from full entitlement to all of the company’s profits and full authority over its key decision making process. On the other hand, creditors feel secure while lending to the company owing to its credibility and transparency in business operations. Finally, since the company is a registered entity and enjoys distinct legal status, regulatory and tax authorities find it easy to monitor its compliance status. Here’s a detailed explanation of all these benefits for your clearer understanding.
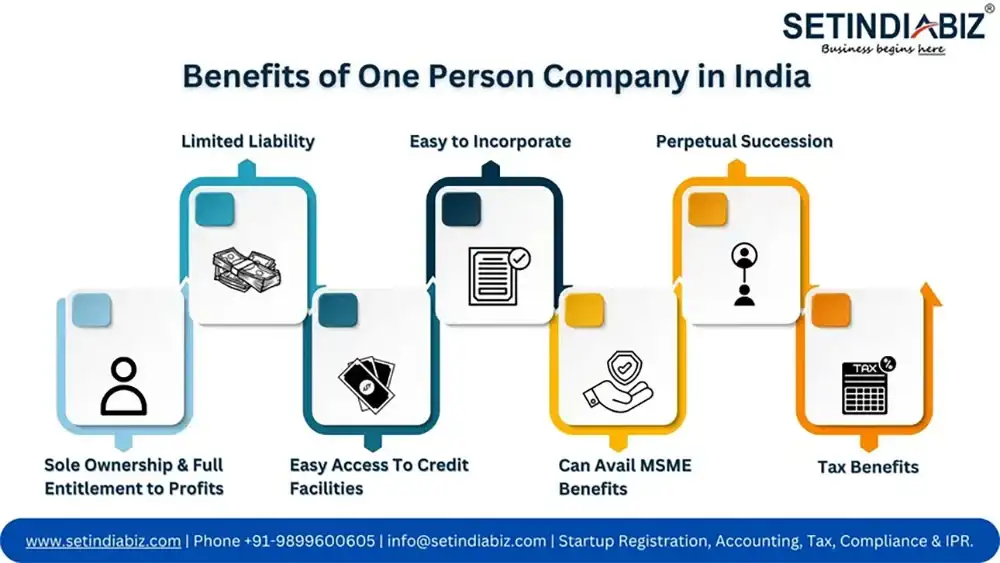
1. Sole Ownership
Sole Ownership is one of the major benefits of One Person Company. The Companies Act of 2013 defines an OPC as a Private Limited Company owned by a single individual only. This individual is entitled to hold all the shares of the company and thereby bring in the entire capital it needs. Since he is the sole investor, he pockets all of the company’s profits as his returns on investment. Sole Ownership offers another advantage as well. It streamlines the decision making process of the OPC and gives its only owner full authority over it.
2. Limited Liability
Limited Liability is one of those benefits of One Person Company that makes it stand out against other single owner businesses like a sole proprietorship firm. Unlike a Sole Proprietorship where the owner’s liability is unlimited, an OPC offers limited liability to its owner. Although the sole shareholder of the OPC is entitled to receive all the income and profits earned by the company, his liability towards paying off the company’s losses and debts is restricted to the unpaid amount of capital he has subscribed to.
3. Easy Credit Facilities
Since an OPC is a legally incorporated entity, its details and documents are available for public viewing and inspection on the official website of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. So, all credentials with which an OPC operates, or applies for credit, can be verified thoroughly. This enhances the credibility and reliability of an OPC and enables it to avail institutional credit facilities with utmost ease and effortlessness.
4. Easy to Incorporate
The introduction of the online SPICe+ application highlights one of the other prominent benefits of one person company. A One Person Company is extremely easy and quick to incorporate since the process is completely online. This has drastically reduced the time and effort that goes into the OPC application process. The SPICe+ application is quite wholesome and provides end-to-end services for OPC formation. You can use the application for name approval of the OPC as well as its registration. Apart from registration, the form also contains various linked forms for EPF registration, ESI registration, GST Registration, and opening a current bank account of the OPC.
5. OPC can Avail MSME Benefits
One Person Companies are usually small-scale businesses and may qualify to be registered as Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises under the MSMED Act. The eligibility criteria for being qualified as MSMEs are based on the limits of turnover and investment of the company in a financial year. Specifically the limits of turnover must not exceed Rs.250 crores in a financial year whereas the limits of capital investment must not exceed Rs.50 crores. Once registered as an MSME, One Person Companies can avail tonnes of benefits offered by the Government to nudge and support the growth of MSMEs. These may include, low-interest loans, collateral-free loans, favorable policies for foreign trade, and credit facilities enabled without any limit on the securities deposited.
6. Perpetual Existence
An OPC can be continued beyond the life of its sole shareholder. This is possible through the nominee of every subsequent shareholder of the OPC. An individual, immediately after becoming the owner of an OPC, is required to choose a nominee who would be succeeding him as the new owner, in the event of his death or his permanent departure. A nominee can be any individual chosen by the owner, and need not necessarily be his legal heir. However, no person can be appointed as a nominee by the owner, unless he gives his consent for the purpose. The consent of the nominee is required to be intimated to the ROC, with the application for updating/replacing the name of the old nominee with the new nominee.
7. Tax Benefits
One Person Company (OPC) offers several tax benefits that make it an appealing choice for entrepreneurs. One of the significant advantages is that OPCs are taxed as separate legal entities, distinct from their owners. This implies that the company’s profits are subject to corporate tax rates, which are often more favorable than individual tax rates. Furthermore, OPCs can also take advantage of various tax deductions and exemptions available to companies. They can claim deductions on legitimate business expenses to reduce their taxable income. Additionally, OPCs can avail of the benefits under the presumptive taxation scheme, which provides simplified tax compliance and lower tax rates for small businesses.
Company Registration Cost
- Director DIN
- Company Name Approval
- Filing Incorporation Forms
- Company PAN & TAN
- Digital Signature
- Drafting MoA & AoA
- Certificate of Incorporation
- 100% Online Process
Disadvantages of One Person Company in India
While One Person Company (OPC) registration comes with several advantages, it is essential for entrepreneurs to be aware of the potential drawbacks as well. As with any business structure, OPCs have their limitations and challenges that entrepreneurs should carefully consider before opting for this legal framework. Let’s explore the key disadvantages of OPC registration, which include limited capital infusion, compliance burden, sole decision-making, convertibility limitations, and restricted business activities. Understanding these potential drawbacks will help entrepreneurs make informed decisions and choose the most suitable business structure that aligns with their aspirations and long-term goals.
1. Limited Capital Infusion
OPCs face restrictions on raising capital since they cannot issue shares to the public. Unlike public companies or private limited companies, OPCs can only be funded by the sole owner’s personal resources or through loans from financial institutions. This limitation can hinder the company’s ability to attract significant investments and restrict its potential for expansion and growth. As the business grows, the entrepreneur may find it challenging to meet the increasing capital requirements, especially if the company aims to undertake large-scale projects or enter new markets.
2. Compliance Burden
OPCs, like other registered companies, are subject to various legal and regulatory compliances. They must maintain proper books of accounts, file annual financial statements, and meet tax and other statutory obligations. The entrepreneur must also comply with company law requirements, such as board meetings, shareholder resolutions, and adhering to the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) norms (if applicable). This can impose a substantial administrative burden on the entrepreneur, consuming valuable time and resources. Failure to comply with these requirements can lead to penalties and legal repercussions.
3. Sole Decision-making
One of the primary benefits of OPCs is that the entrepreneur has complete control over decision-making. However, this advantage can also be a disadvantage, as it may lead to limited perspectives and ideas. In larger companies with multiple stakeholders, diverse viewpoints can lead to better decision-making and creativity. In an OPC, the entrepreneur might face challenges in seeking objective feedback or may lack the necessary expertise in certain areas, potentially impacting the overall growth and success of the business.
4. Limited Business Activities
The Companies Act, 2013, restricts certain business activities that an OPC can engage in. Activities such as non-banking financial investment or charity under Section 8 of the Companies Act are not allowed for OPCs. These limitations can impact the entrepreneur’s ability to diversify the business or venture into new sectors. As the business evolves, the need for expanding into related or different areas may arise, and the constraints on business activities can become a significant drawback for the entrepreneur.
Conclusion
One Person Company (OPC) registration offers unique advantages, such as limited liability and individual ownership, making it an attractive option for solo entrepreneurs and small business owners. The benefits of reduced compliance requirements, tax efficiencies, and the ability to maintain complete control over decision-making add to its appeal. However, entrepreneurs must also be mindful of the limitations, such as restricted capital infusion, compliance burdens, and restrictions in business activities for substantial growth. By carefully considering both the benefits and disadvantages, entrepreneurs can make an informed decision whether to go for OPC registration or not. Seeking professional guidance during the registration process can further enhance the entrepreneur’s understanding and ensure a smoother journey towards building a successful and legally compliant OPC.

